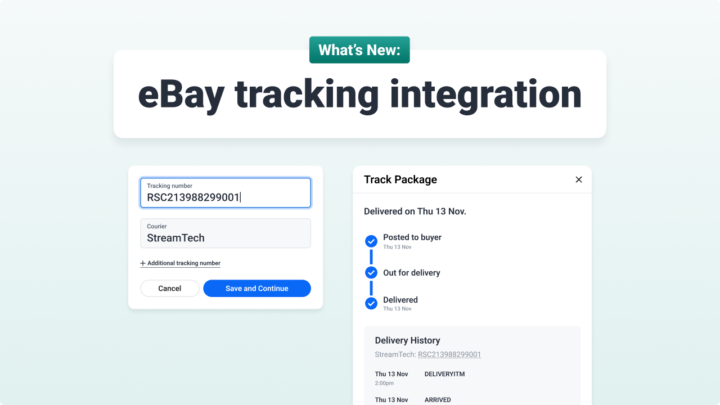
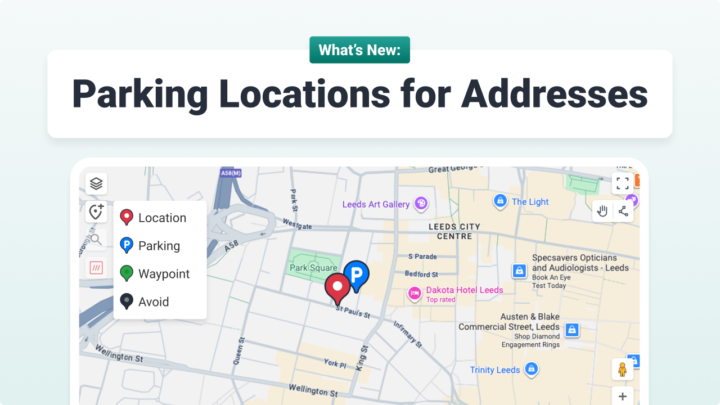
The final leg of your delivery journey is often referred to as the ‘last mile,’ or ‘final mile’. This is one of the most important stages of your logistics operation as it can often be the only time your customer has a personal interaction with your brand.
Katja Busch, Chief Commercial Officer of DHL, emphasized the importance of the last mile in ecommerce explaining that it can greatly impact a brand’s reputation.
‘The last mile is a key differentiator in ecommerce – it’s the one physical touchpoint between brand and consumer. This final stage is where online shopping meets reality. It’s the moment of truth for retailers and logistics providers, a chance to leave a lasting impression on the customer.’ – DHL
And that ‘lasting impression’ isn’t always positive.
A consumer sentiment study by Descartes revealed a significant challenge facing the ecommerce industry: delivery failures.
The research found that two-thirds of consumers have faced delivery problems. These include missed or failed deliveries.
Among those affected, 68% took action.
This led to negative consequences for the retailer or delivery company.
The impact of these issues extends beyond mere inconvenience. Dissatisfied customers may develop negative perceptions of both the courier and the retailer, which can dissuade repeat business.
This can be very harmful for online businesses. Marc Vukovic, a business development manager at Zetes, explains that “customers may not complain. They might just switch to another online retailer.”
And the last thing any business wants is to lose customers to a competitor due to a bad delivery experience.
We looked at how bad delivery experiences affect customers earlier in the year with a ‘fireside chat’ with Brightpearl, a top retail operations platform, and Scandinavian House when we discussed “The Benefits of Managing Furniture Wholesale & Distribution In-House.”
With this in mind, what are the key challenges of last mile delivery, and how are businesses looking to overcome them?
The key challenges of last mile delivery
Your last mile delivery is often the most complex and costly. Many factors contribute to this, such as urban congestion, environmental concerns, and rising customer expectations. Below is a detailed look at these main challenges.
We will also share examples of solutions that are improving the last mile delivery experience.
Urban congestion
Urban congestion poses a significant challenge to the efficiency and reliability of delivery services worldwide.

Traffic jams, limited free parking in city centres, and general congestion can cause delays. This can lead to late deliveries and even missed deliveries – all of which can also increase your operational costs.
Delivery companies can struggle to meet delivery timeslots when congestion is particularly high. Customers can become dissatisfied, causing a potential loss of business.
To reduce traffic in cities, businesses are looking at new options including electric vehicles, cargo bikes, micro warehouses, and delivery drones.
They are using the latest route planning software and commercial vehicle GPS apps. This helps them plan efficient delivery routes and their drivers can also avoid busy roads.
If you want to understand how traffic impact late deliveries, this article is for you: “How Does Traffic Affect Delivery Times?“
Rising consumer expectations
Research shows that consumers now expect fast, reliable, and flexible delivery options. This includes same-day and next-day delivery. These expectations apply to all businesses, no matter their size.
McKinsey & Company reports that 90% of consumers want their deliveries in two or three days while 30% expect same-day delivery.
This puts more pressure on retailers to quickly turn orders over quickly. They need to fulfill orders fast and deliver them efficiently, especially when handling large volumes.
It is not surprising that quick commerce is growing fast.
This growth matches rising consumer expectations for deliveries. Quick commerce, or Q-commerce, is about delivering goods to customers quickly – usually within an hour or less.
Environmental impact
More delivery vehicles on the road lead to air pollution, traffic jams, and greenhouse gas emissions. This has caused many couriers to use eco-friendly delivery methods, such as electric vehicles and e-bikes.
The World Economic Forum found that delivery vehicles in the top 100 cities will increase by 36% by 2030.
As a result, emissions from delivery traffic will go up by 32%. Congestion will increase by more than 21%. This means each passenger will spend an extra 11 minutes commuting every day.
Additionally, the packaging materials used for shipping products often end up in landfills, contributing to waste and environmental degradation.
Research found that ecommerce generates 4.8 times more packaging waste than traditional brick-and-mortar shopping.
To address these issues, companies are exploring sustainable packaging solutions, such as recycled and biodegradable materials.
Emerging delivery trends and solutions that are tackling these key challenges
The “last mile” is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer expectations. Let’s explore some of the key trends shaping the future :
Parcel Lockers

Parcel lockers have emerged as a game-changer in the logistics industry. These secure, self-service stations offer customers the flexibility to pick up their packages at their convenience, often 24/7. Parcel lockers combine multiple deliveries into one location. This helps lower operational costs, improve delivery efficiency and reduce the environmental impact.
Quick commerce & innovative warehousing
Services like Deliveroo and Uber Eats have made quick commerce popular coupled with the rise of small / micro warehouses in urban centres.
These warehouses help with fast order fulfilment and delivery, especially for quick commerce services. These facilities use AI and robotics to rapidly fulfil orders, enabling deliveries in as little as 10-15 minutes.
Even grocery stores like Co-op have entered the quick commerce market. They do this by partnering with apps like Deliveroo, Just Eat, Uber Eats, and Amazon.
These apps handle payments and fulfill orders for Co-op. This lets customers get their orders quickly. The company has lofty ambitions to expand its share of the quick commerce market by more than 30% over the next four years.
“Co-op aims to grow its share of the quick commerce market. This will be done through our online platform and with strategic partners,” says Chris Conway, Co-op ecommerce director:
“More than 80% of the UK population now has access to Co-op groceries online.”
Logistics technology
Logistics businesses can use various software to manage their last mile operations more efficiently and effectively, including Transport Management Systems (like Stream), which streamline deliveries and collections, boost efficiency, reduce cost and enhance customer satisfaction.