DHL recently published a report outlining some of the key logistical challenges that complicate last-mile deliveries, whilst presenting solutions to these challenges that evolve the final leg of delivery so that it’s fast, cheap, reliable and green.
The answers can be found in a diverse selection of emerging logistics solutions and trends, with logistics and delivery management applications being at the forefront of this evolution.
Other solutions alluded to include: micro-fulfilment centres (otherwise referred to as ‘dark stores’), quick commerce and alternative delivery vehicle methods (such as e-cargo bikes and boats), whilst challenges such as urbanisation and excessive pollution continue to plague the sector.
Successful last-mile logistics ultimately means knowing what’s available and how to successfully utilise these current and future trends.
First and foremost however, a clear understanding of what ‘last-mile’ means in logistics is needed, in addition to clarity surrounding the challenges ecommerce and shipping businesses face at the most important stage of the supply chain.
What is last-mile delivery?
While the ‘last mile’ doesn’t specifically relate to an imperial measurement when it comes to deliveries, what it does refer to is the final leg of a journey for a package or parcel for delivery.
This will often be considered as the stage where a package leaves a warehouse or depots after typically being passed from a manufacturer, to a warehouse, and then to a local fulfilment centre.
The package is then transported to its final destination – most commonly the customer’s doorstep or an out of home delivery location, such as a parcel locker.
“The last mile is a key differentiator in ecommerce – it’s the one physical touchpoint between brand and consumer.” – Katja Busch, Chief Commercial Officer, DHL
Most consumers are familiar with this stage of the logistics process due to tracking an order after purchasing a product online from a retailer.
For retailers and logistics companies, the key aim is to successfully provide this service in a way that is simultaneously fast, cheap, reliable and green – all of which pose a broad depth of challenges and logistical headaches that must be overcome in order to increase market share, enhance customer service, and generate profit – particularly in a competitive post-Covid ecommerce sector.
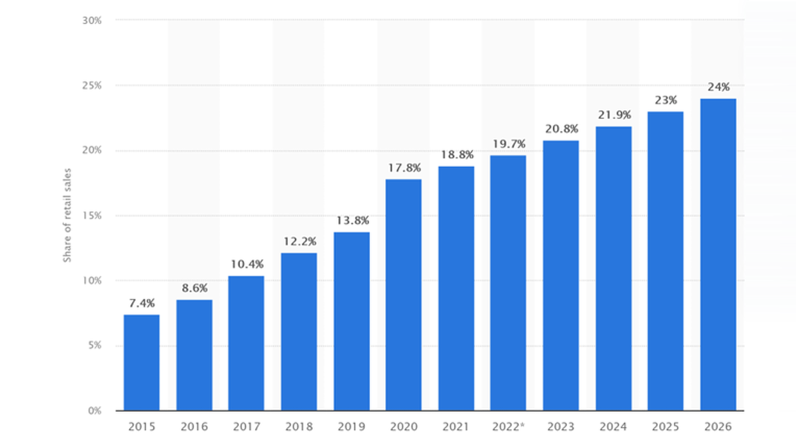
Ecommerce as a percentage of total retail sales worldwide, 2015–2026 (projected). Source: Statista 2023
As ecommerce sales are predicted to continue trending upwards worldwide post-Covid, more last-mile delivery challenges will come to the fore and inventive solutions to these challenges are needed.
The pressing question is therefore: what are the emerging trends that address the most pressing challenges the last-mile poses?
How logistics and delivery management applications have transformed last-mile delivery for the better
Logistics and delivery management applications, such as Stream, help to solve the four imperatives of last-mile delivery logistics: fast, cheap, reliable and green:
- Fast – same day delivery and next day delivery options are becoming increasingly popular among shoppers
- Cheap – preferably delivery is free of charge or minimal
- Reliable – customers successfully receive their delivery within a given time frame & undamaged
- Green – alternative packaging options and green transport options (decarbonisation) are becoming increasingly popular
So here are the four imperatives broken down into further detail as we assess the common challenges associated with them, and how Stream helps to effectively solve them.
Fast, cheap and green
“Studies consistently show that orders with a delivery time over two days are often not completed. Amazon changed the game with the same-day delivery option.
Then came food apps, which boomed during the pandemic and introduced us to on-demand delivery, also known as quick commerce.” – DHL
The old adage ‘time is money’ rings true when it comes to the last-mile of logistics.
Customers want their goods delivered as quickly, and as cheaply, as possible and retailers want this to be a reality on their end too.
Throughout the last-mile, that means getting from point to point in as little time as possible, so there are a number of common challenges pertaining to route planning and route optimisation that commonly hinder the efficiency of this process:
- Planning routes manually (using paper delivery notes, excel spreadsheets, Google Maps etc) takes up a lot of time for logistics staff, which can be costly.
- Routing is often done based on a Transport Planner’s personal knowledge of the area, creating a key-person dependency when that person is out of office or leaves an organisation.
- Manually planning large volumes of orders, which result in a large time commitment for planning staff each day.
- All of the above create difficulties for meeting required delivery dates and times as soon as possible.
Using route planning and optimisation software is a sure-fire way to address all of these challenges.
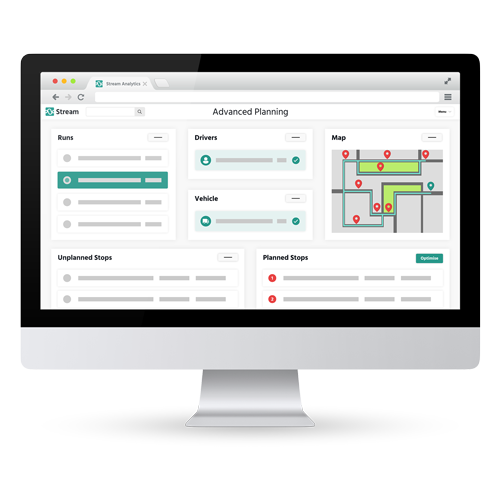
Stream enables you to plan the most efficient and economical delivery routes for a fleet, taking into account all locations, total route times, vehicle capabilities (such as capacity, weight, cube etc). Quickly make the most of given resources and deliver on time to customers.
In addition to planning routes, Stream automatically optimises the planned routes at the click of a button.
Multi-drop delivery runs can be sequenced in a matter of seconds to produce the shortest route possible based on mileage, reducing the time delivery vehicles ultimately spend on the roads and the number of wasted miles for your vehicles and drivers.
All of these functionalities boost efficiency, save time, cut costs and reduce a fleet’s carbon footprint.
Reliable
“The customer’s first interaction with a product is when it arrives at their doorstep, so last-mile logistics planners need to ensure that goods arrive on time and undamaged.” – DHL
Real-time tracking, proactive delivery notifications and electronic Proof of Delivery have all transformed last-mile delivery in a variety of ways to help businesses meet ever-growing consumer expectations, and enhance the overall transparency, reliability and efficiency of delivery day.
All of which culminate to help ensure that the customer’s goods successfully arrive within their delivery window (particularly when paired with route planning and optimisation), and to the correct recipient, and in perfect condition.
Particularly since the Covid-19 pandemic, as customers have become more accustomed to shopping online and being offered a variety of delivery options, they (as well as the business sending the goods) want to know know in precise detail:
- Where the package and delivery driver are located at all times
- The exact time the order will be delivered
- The various options available if the delivery cannot be successfully made
Each point creates various logistical challenges for the companies that are delivering the goods:
- Customers chasing support for delivery updates via phone/email, taking up time and resources in the process
- Staff have to manually contact customers to inform them of delivery windows prior to a delivery taking place, costing valuable time
- The sender may not be able to see a driver’s progress, and be notified of any issues throughout the day causing delays or packages to be unsuccessfully delivered
- The sender may not have access to historic tracking information or Proof of Delivery in the event of a customer dispute (ie, if a parcel was delivered to the wrong address)
So how do logistics and delivery management applications solve these challenges?
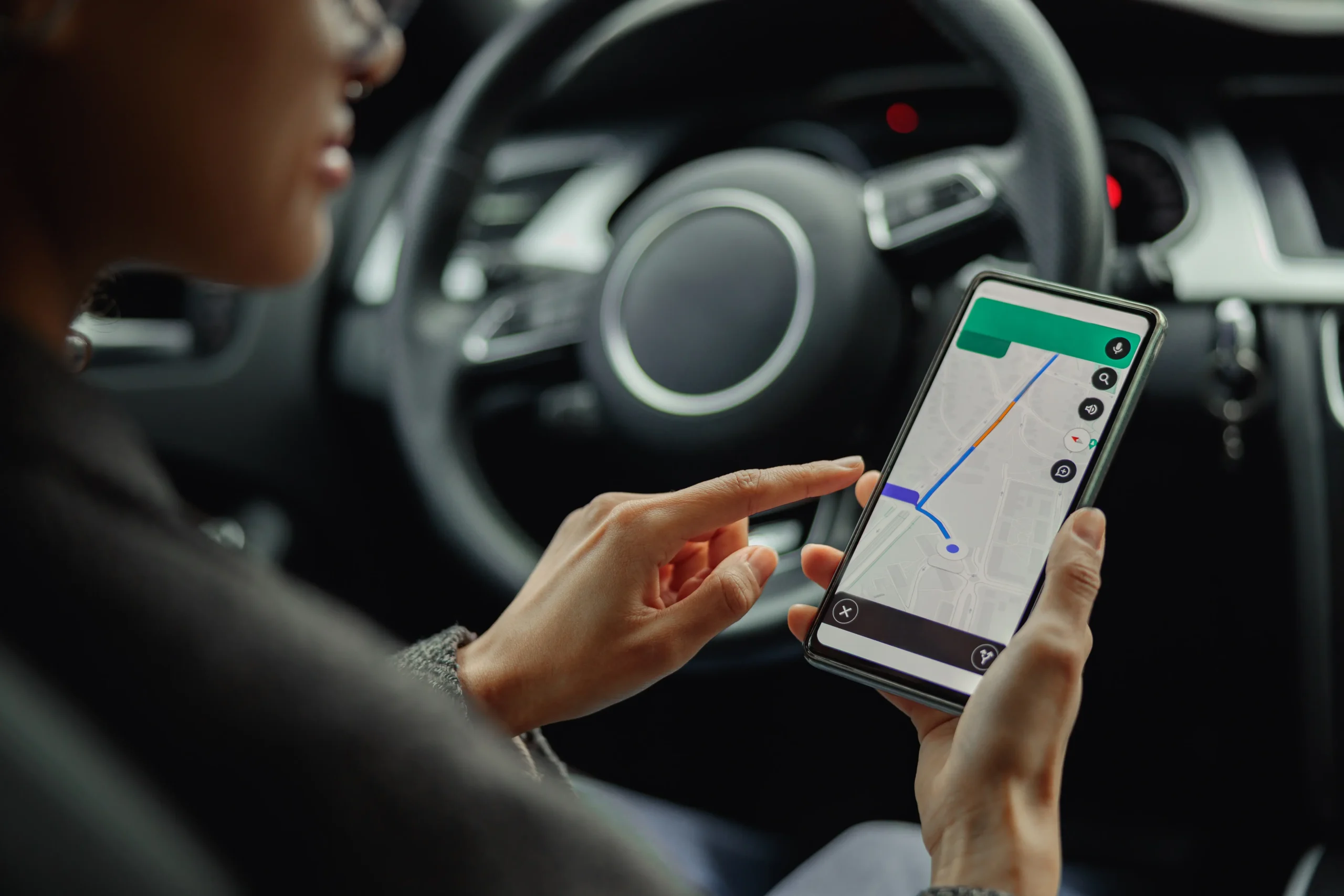
Real-time delivery tracking information for customers has become an industry-wide standard in retail, and it plays an integral role on the day of delivery as it offers recipients full visibility over their order.
This allows them to anticipate its arrival if they are unavailable to receive the package at any point, saving both time and money that would be otherwise wasted on re-delivery.
![]()
Pairing real-time delivery tracking with email and SMS delivery notifications (check out our previous post on the best channels for sending delivery notifications) adds even further reliability, as the customer is proactively updated with the latest information where it is most likely to be seen.
On the day of delivery, live tracking information frequently updates with precise ETA’s, the driver’s current location (tracked via GPS), and how many stops away the driver is from the delivery stop.
It’s all about keeping the customer up to date and informed throughout the entirety of that last-mile.
On the flip side of the coin, live tracking allows the sender to access monitor screens which are used to oversee each driver’s progress throughout the day.
This allows companies to see the drivers’ current location and progress in order to monitor their performance versus the planned ETA’s. This also gives visibility over any issues, such as a part or failed delivery.
Tracking information is then saved in the cloud for each and every order, which can be viewed days, weeks or months after a delivery has been completed.
For delivery events, applications such as Stream will capture the drivers latitude & long coordinates, so you can see exactly where they were when they completed a delivery, as well as capturing an electronic Proof of Delivery signature or photograph.
This can help protect senders against fictitious customer disputes, or resolve issues where an address might be incorrect.
What other last-mile delivery trends are revolutionising the industry?
Parcel lockers
Secure drop-off locations such as parcel lockers are a crucial component in reliable last-mile delivery.
Parcel lockers offer customers the convenience to pick up their packages from a nearby secure locker, which are generally accessible 24/7.
This helps to solve the problems that many last-mile logistics providers face — especially in highly-populated urban cities — that affect their productivity, efficiency, and expenditure.
It makes perfect sense for logistics companies, as they only have to make one delivery to the lockers, mitigating the risk of unwanted additional costs and inefficiencies caused by unsuccessful deliveries.
Retailers and logistics service providers can also aggregate multiple parcels/deliveries into a single locker station which is much more cost effective, efficient and eco-friendly than delivering to multiple locations.
Solutions to urbanisation: cargo e-bikes and boats
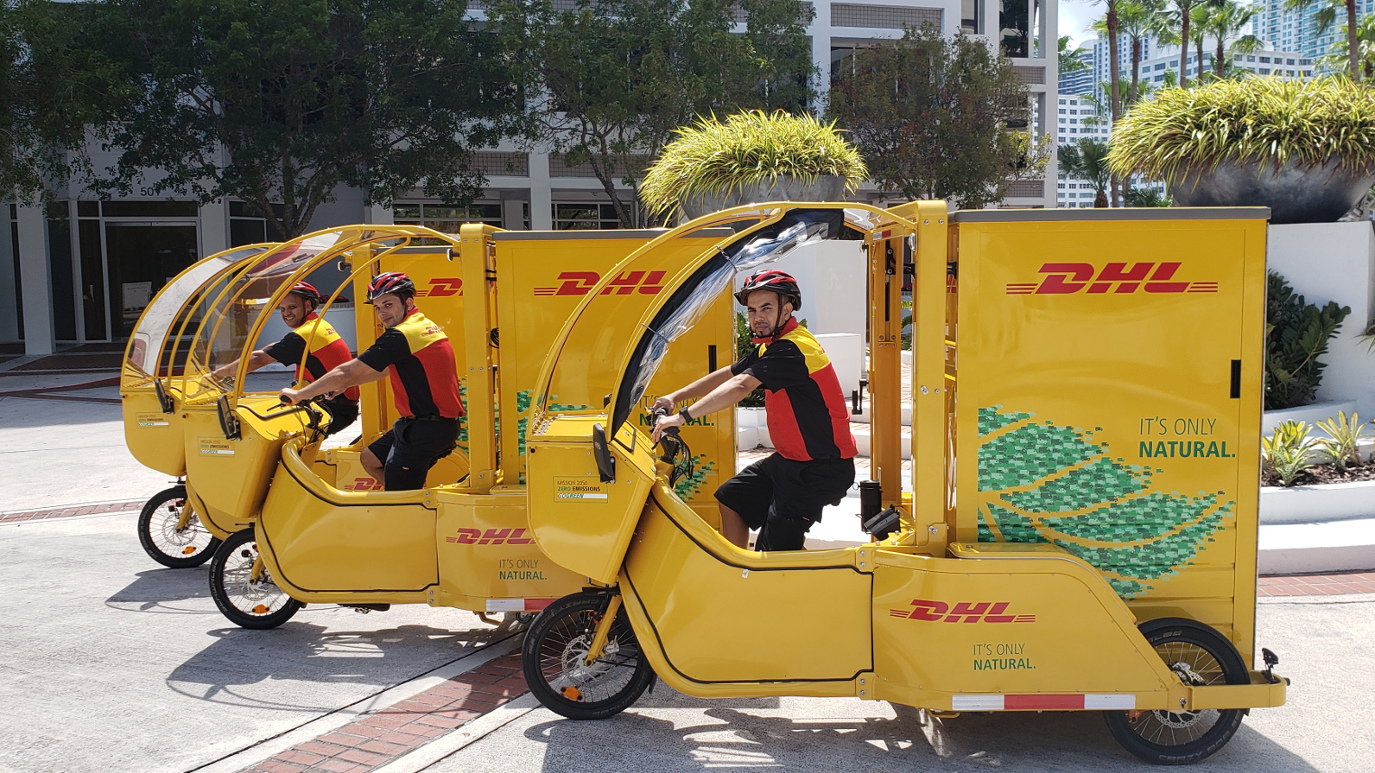

DHL e-cargo bikes. Source: DHL
Urbanisation is an unstoppable trend, particularly as cities already contain 56% of the world’s population and account for 80% of global GDP.
By 2050 68% of the world’s population is expected to be urban, increasing the concentration of deliveries within these locations.
This means that last-mile logistics is overwhelmingly urban logistics, and conventional delivery trucks and vans will still be the norm, but evolution in this space will be required.
Alternative drivetrain solutions such as cargo e-bikes and boats will offer green solutions that may prove to be faster, cheaper, and more reliable than current conventional delivery trucks or vans.
Quick commerce & dark stores
During the pandemic, the rise of fast food and grocery delivery services such as Deliveroo, Uber Eats and Gorillas introduced us to instantaneous on-demand delivery known as quick commerce.
Last-mile deliveries for quick commerce are typically facilitated by ‘dark stores’, which are micro–fulfilment centres located in densely populated urban areas that use smart technology such as predictive product selections and autonomous robots to rapidly fulfil orders so that they can be delivered in as quick as 10-15 minutes.
Conclusion
To conclude it is evident that technology is playing a pivotal role in evolving the last mile of logistics: from smart logistics and delivery applications to advanced dark stores, technology continues to permeate the last mile.
The distance covered over the last mile continues to shorten too, as logistics companies situate themselves closer to the customer than ever before – reducing all of the imperatives of last mile logistics: fast, cheap, reliable and green in one fell swoop. This is more evident than ever through the emergence of quick commerce, dark stores and parcel lockers, which are tactically placed in densely populated urban areas.
Want to learn more about how Stream can solve your logistical challenges?
Frequently Asked Questions
While the ‘last mile’ doesn’t specifically relate to an imperial measurement when it comes to deliveries, what it does refer to is the final leg of a journey for a package or parcel for delivery. This will often be considered as the stage where a package leaves a warehouse or depots after typically being passed from a manufacturer, to a warehouse, and then to a local fulfilment centre. The package is then transported to its final destination – most commonly the customer’s doorstep or an out of home delivery location, such as a parcel locker.
Stream offers proactive email and SMS messaging notifications (available as an add-on) so that businesses can keep their customers informed throughout the final mile delivery process. Delivery notifications include information based on specific order events, such as ETAs and delivery slot times.
Stream enables businesses delivering goods and products in their own vehicles with the most efficient and economical delivery (and collection) routes – including last mile deliveries.
Route planning in Stream takes into account a number of criteria to calculate optimised multi-drop final mile deliveries, including all delivery locations, total delivery times and vehicle capabilities, including capacity, weight and cube etc to produce the shortest route possible based on mileage, reducing the time delivery vehicles ultimately spend on the roads and the number of wasted miles for your vehicles and drivers.








