A recent study by Zebra Technologies, has assessed how next generation wireless technologies 5G and Wi-Fi 6/6E will impact enterprises, and their current suitability for businesses to migrate to.
Both bring a plethora of benefits to businesses that frequently use web and mobile based applications – understanding their application roadmap and the availability of 5G and Wi-Fi 6/6E in their local area will help enterprises to determine if, how and when to begin prioritising them.
What’s driving 5G adoption, and what are its benefits?
The promise of blazing fast 5G speeds is driving consumers to buy 5G devices in droves, at such a rate that 5G is the fastest growing mobile technology in history.
To put this growth into context, it took 5G a year to achieve 225 million users, whereas 4G LTE took four years.
5G’s growth is predicted to continue being exponential – in 2026 the number of worldwide 5G subscribers is predicted to hit 3.5 billion, representing a 57% annual growth rate over 6 years.
There are numerous factors that can be attributed to its successful growth and popularity.
First and foremost, 5G adoption benefits everyone – from service providers to the end user.
Service providers benefit from improved device sales, a more efficient and reliable infrastructure, and reduced costs. Both the service providers and the end user benefit from greater use cases, improved speeds and lower latency performance. It’s a win-win situation for all of the stakeholders within the 5G ecosystem. In an enterprise environment 5G will help improve existing applications and drive the deployment of new enterprise applications- essentially laying the foundations for greater innovation.
So what elements of the 5th generation mobile network have been improved? And how do these improvements benefit enterprises?
There have been five key areas that have seen significant improvement when compared to 4G: speed, latency, energy reduction, bandwidth, signal quality and signal strength.
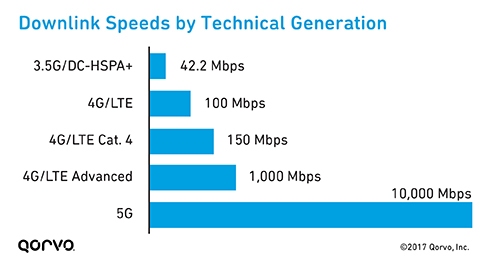
5G has the potential to provide speeds up to 10 gigabytes per second, which is comparable to wired speeds, and 10-100 x faster than 4G LTE. This is compounded by the lower levels of latency found in 5G, allowing information to pass from mobile devices to servers at faster rates.
This combination provides the necessary speeds for real-time applications, such as autonomous vehicles, that instantaneously process and relay information to function.
The bandwidth of 5G has seen a similar seismic improvement, enabling it to support 100 x more devices than 4G LTE. This equates to one million devices per every square kilometre, enabling large ‘always connected’ areas with improved signal strength and quality.
All of these improvements do not come at the cost of high energy consumption levels either, making it an environmentally friendly, green alternative to 4G LTE. 5G’s network is so efficient that it has the potential to reduce overall energy consumption per unit of traffic by up to 90%.
How will 5G shape the future of applications within logistics, retail and healthcare?
Transport and Logistics
Through the power of 5G coverage, large facilities such as airports and train stations can more effectively deploy mobile solutions.
Solutions such as baggage sensors which track luggage in real-time so that they are easily located and processed, limiting the chance of them being misplaced or lost in transit.
The same premise can be applied to the logistics and pharmaceutical industries – sensors can be placed on refrigeration units in delivery trucks to ensure correct temperatures are maintained throughout shipping for sensitive pharmaceuticals, frozen foods and more.
Retail
In retail 5G has been used to create virtual reality ‘smart mirrors’, also referred to as ‘digital mirrors’ or ‘smart displays’, where shoppers can try on virtual clothes and experience personalised fashion suggestions in real-time. 5G powered AR (augmented reality) software allows shoppers to try on virtual products through an instantaneous and vivid interactive fitting experience without visiting a traditional dressing room.
Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, 5G allows patients’ diagnostic data to be streamed in real-time from the field or ambulances to emergency rooms so that they receive information instantaneously, allowing them to prepare ahead of time, even in remote areas. Large files (over 1GB) that contain critical information in the form of scans or high-quality images can be transferred from different entities in minutes as opposed to hours without impacting network performance or availability, eliminating delays in busy areas such as hospitals where 4G connectivity can be negatively impacted by large congregations of people.
Conclusion
5G is currently in a transition period, meaning that the infrastructure is still in its infancy and has yet to be established across large parts of the UK and US, particularly in rural areas. It is therefore mostly accessible in densely populated cities where the technology is needed most.
In rural areas where there is a distinct lack of 5G coverage, connectivity reverts to 4G, which has negative implications for applications which require the fast download speeds, high bandwidth and low latency levels of 5G. These implications impact work productivity and, in more extreme instances, safety.
Workforces can continue to use 4G until their enterprise has more use cases for 5G and it is fully accessible. Businesses should then assess their devices and whether or not they are 5G ready, and decide if they are using their applications to their full potential.
What’s the importance of Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E to businesses, and how does it differ to Wi-Fi 5?
“Wi-Fi 6 delivers what everyone wants — enterprises and users alike — more of everything. More speed. More capacity. More responsive applications. More battery cycle time. And more security.”
Enterprises are increasingly utilising IoT (internet of things) mobile solutions to bolster productivity and connectivity throughout their workforce. In a similar vein to 4G, as more devices are connected to a single Wi-Fi network, congestion occurs, leading to reduced speeds and connectivity issues.
Wi-Fi 6 is able to accommodate more devices, connections and traffic without this hindering performance due to enhanced bandwidth capacity and reduced latency. Businesses can therefore deploy more IoT devices among their workforce to create new levels of business intelligence and improve accessibility to technologies such as augmented reality, which have the benefit of improving accuracy and productivity.
In logistics Wi-Fi 6 enables workforces based in warehouses to use augmented and virtual reality applications to visually direct them via the fastest path to the right location to pick items for an order or put away incoming inventory — and verify that the correct items were picked or placed on the shelf for storage. Wi-Fi 6 also makes it easier to track and trace all inventory — from incoming raw materials to outgoing finished goods.
All of these functionalities are achieved through significant improvements to the Wi-Fi’s speed, bandwidth, latency, efficiency and security.
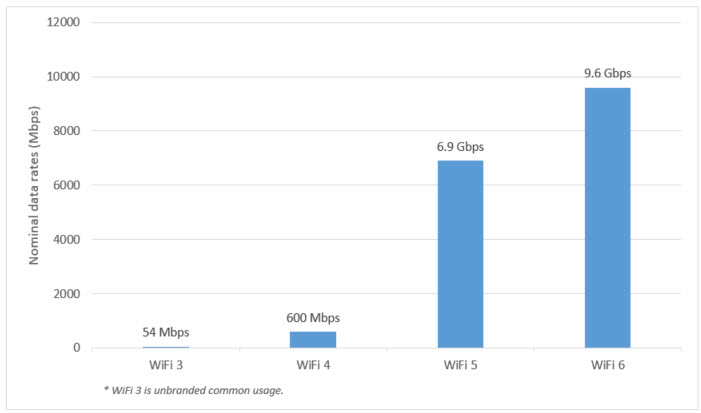
Wi-Fi 6 offers much faster data rates. Where Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) maxes out at 6.9 Gbps, Wi-Fi 6 offers a maximum possible data rate of 9.6 Gbps, providing support for more bandwidth-intensive applications.
Compared to Wi-Fi 5, Wi-Fi 6 quadruples bandwidth and capacity, reducing congestion and interference throughout the network, particularly in denser user environments such as stadiums where there could be tens of thousands of people connecting to the Wi-Fi. And with substantially reduced latency (75% lower, according to Intel), a substantial increase in devices and traffic won’t impact application performance, improving workforce productivity.
Wi-Fi 6 also gets a security upgrade thanks to WPA3, which uses the latest security protocols, enabling stronger authentication and increased cryptographic strength through longer encryption keys. These added layers of security are ideal for markets with sensitive data, such as healthcare and retail.
Conclusion
In order to assess whether or not an enterprise should be prioritising Wi-Fi 6 there are numerous factors that require consideration. What are their application needs and will future applications need Wi-Fi 6 to be leveraged to their maximum potential? How accessible is Wi-Fi 6 in the area?
Understanding their application roadmap and Wi-Fi 6’s accessibility will help enterprises determine if, how and when to initiate the upgrade path. Certain enterprises may not even require Wi-Fi 6 and can suffice with Wi-Fi 5, particularly enterprises with small workforces who are less reliant on advanced technologies.
Frequently Asked Questions
5G is the fifth and latest generation of mobile network which provides greater download speeds, reduced latency and a wider coverage range in comparison to its predecessor 4G.
Wi-Fi 6 (also referred to by its technical name ‘802.11ax’) is the sixth and latest generation of the Wi-Fi network protocol. Wi-Fi 6 improves on its predecessor through greater download speeds (around 30% faster) and less bandwidth congestion, making it more efficient and reliable in comparison to Wi-Fi 5.
IoT (Internet of Things) devices are hardware devices, also referred to as smart devices, such as sensors, computing devices, appliances and cameras that connect to the internet to send and receive data. Businesses can utilise IoT devices to allow for the passing of data autonomously between one another without human interference, thereby reducing manual processes – saving time and money.







